New to Usenet
From Newsbin
Quick Links: Version 5 Documentation | Version 6.60 Documentation | Newsbin Home | Latest Newsbin Release | Glossary | Newsbin Forums
Usenet is not the Web, it actually existed before the Web was created.
Usenet is a collection of discussion groups, called newsgroups, where people can share information on topics described by the newsgroup name. For example, alt.binaries.pictures.autos will have pictures of cars along with some discussion about cars. There is very little control over what is available on Usenet, and the content is uploaded by users all around the world. Newsbin focuses on downloading binary content from Usenet, similar to P2P file sharing applications. The difference is, the content comes from commercial news servers that share information with each other around the world, instead of from a network of individual computers. You can download things faster from Usenet and there is no requirement for you to contribute content in order to download content.
You’ve heard there's something good to get here. We think so. Newsbin has been around since 1995 with major upgrades almost every year and we're still improving the product every day. Newsbin will make sure the binaries you are looking for get to your PC reassembled and ready to use. It will maximize your PC and internet connection to get it down to you fast!
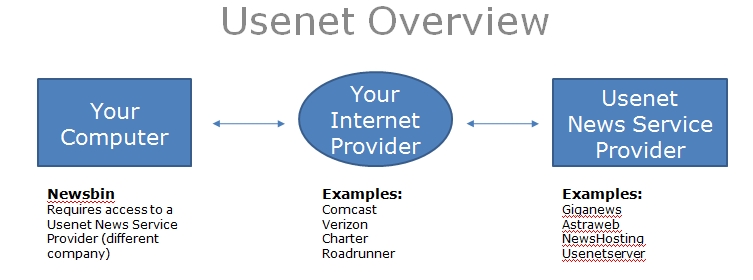
Usenet is a Client/Server based technology and Newsbin is your Client. Newsbin needs a connection to a news service to get you going. That's the first step into the world of USENET. Grab a trial account somewhere and be ready to enter your user name and password. Picking the right service is based on how much and what type of data you will be downloading. The services are primarily sold by quantity of data downloaded per month and number of days worth of data the server stores (retention). For now, you are new to this and probably can't assess what your usage will be. Once you’ve gone through some tutorials, poked around a bit and see what's available, you will be better able to decide which service works best for you. Just grab a free trial with one of the major news service providers and get ready to install Newsbin.
There is an excellent resource discussing Usenet at Harley Hahn's Usenet Center and in particular Harley Hahn's Orientation to Newsbin. You can also see tutorials on usenet at Giganews Usenet University.
Newsbin is a very feature rich program with extensive documentation. The following basic concepts should get you going, but you will want to do some reading to get to know these many features and how they make using newsgroups much easier.
A minimum list of terms you need to know for using Newsbin are:
News Server
A news server stores posts in newsgroups. You either pay for a quality news service that carries more newsgroups and retains posts for a longer amount of time or you get free access from your internet service provider (although not all ISP's provide News Servers). The pay services issue an account username and password when you sign up. This username and password is entered into NewsBin so you can access the news server and download posts. We currently have special pricing for Newsbin users arranged with UsenetServer.
Newsgroup
Or just Groups - categories that organize where certain content is posted. For example alt.binaries.pictures.autos should only have pictures of cars in it. Groups containing the word "binaries" typically contain posts with encoded attachments representing binary files such as images, music, movies, or programs. You manage the groups you subscribe to in the Add Groups dialog.
Post
Can be used as a noun or a verb. It is either a specific representation of information available on the news server, or the act of putting information on the server. For example "I just downloaded a post that had a great picture of the new 'Vette" or "Can you please post a picture of a new 'vette?".
Messages have a size limit. If a large File is posted, it needs to be chopped up into smaller Parts and each part posted separately. Each part has a unique subject with special numbering to indicate it is part of a set. This is called a Multi-part post. NewsBin automatically combines these so you don't have to.
Posts and Messages may also be referred to as Headers which would not be entirely correct. A Header is just the top part of a post.
Header
This is the top portion of a message that includes the subject, date, poster email address, and other information to uniquely identify the post to NewsBin. You can download headers to see what posts are available in the newsgroup or you can use the Internet Search feature to see headers related to your search from our Usenet Index.
NewsBin combines related headers onto one line in the cases where they represent a Multi-part post.
Post List Tabs
When you open a newsgroup in Newsbin, a new tab for that group's post list opens. Newsbin loads the current headers into memory for you to filter and find the stuff you want to download. These tabs are where you pick files to download.
Downloads Tab
This tab shows the status of the files you are downloading in real time.
Files Tab
This tab is a list of files you’ve downloaded and where they are stored.
Logging Tab
These are messages that show success or failure during download progress. Logging messages are shown in reverse chronological order (latest at top). Check here after a download if files show up in the "Failed Files Tab". In versions prior to 5.53, this was called "Status".
Failed Files Tab
This tab holds files that failed to download or reassemble. Reasons vary, usually it's due to a server configuration error, a firewall blocking Newsbin, or a post that is no longer on the server. As you get to know the process you'll understand these and how to find a working post.
Indexing Database and Searching
Due to the uncensored nature of Usenet, organization is not simple. There are service providers that read across the major newsgroups and index the content as best as can be done. Newsbin provides an optional indexing service and embeds the technology in the user interface under the Search Tab. It is offered for as little as $2.50 per month. More information on the Internet Search page. You can search for content by keywords and the search can cross groups to find what you are looking for.
NZB
Files that define the contents of complex, multipart posts so that all parts can be retrieved more simply in one session. These files are generated by a number of different Usenet Indexing Services. Some are free and some charge a subscription fee. Newsbin can read and can create NZB files.
Data Rate
One thing that often is confusing to people who are not familiar with usenet is the different ways that data rates are often quoted.
There are two value one comes across:
- Bits per second: This is the rate that is normally quoted by ISP's. If one is using a modem this figure is often quoted as 'baud', although this seems to have fallen into disrepute for broadband links. This figure should always be considered as the maximum that is possible, and one normally expects to fall a bit short. With a cable broadband link typical speeds are in the range 80-100% of the maximum speed. With ADSL links figures in the range 25-50% are not untypical although better rates can be achieved if one is near enough to the exchange providing the service.
- Bytes per second: This is the reate that is more meaningful to users as it represents the rate at which they see data appearing on their hard disks. File sizes are quoted in Bytes (10 k, 10 mg, 10 gig...). Each byte consists of 8 bits, and there can be a small protocol overhead as well.
By convention a lower case 'b' is used to represent bits per second and an upper case B represent bytes per second. However there is often confusion as many people mix up their use of upper and lower case 'b' so one has to work out what is meant from the context.
If one therefore takes a notional 10Mbps that is the figure quoted by an ISP. In practise one rarely achieve the full quoted speed, so a more realistic value of what might be achieved is 9Mbps (bits per second) if using a cable broadband connection. When one translate such a figure to bytes this would be around 1.1MBps (Bytes per second). You'd expect a 10 mg file to download in around 10 seconds.
Newsbin tries to help you by quoting the speeds it is achieving in the status bar using both conventions. In the example mentioned above the figures would look something like 9Mbps/1.1MBps.
What's Next?
Newsbin downloads content from your News Server. It allows you to subscribe to as many newsgroups as you want and looks in the groups to download headers for posts so you can choose what you'd like to download to your pc. Newsbin can also download based on an NZB file or a Search of newsgroups without having to subscribe to groups or to download headers. After you install Newsbin, read through the Running Newsbin for the First Time document and you should be on your way to enjoying Usenet Newgroups.
Why Buy Newsbin
We hope you will think that the one time license fee is a HUGE bargain. You get all future updates, so it is just this one time fee. You also will have a voice in making the product better. You will get good advice and technical support from the Newsbin developers and the user community. And it is the fastest and most mature product available. You’ll forget about the license fee you spent in about an hour! Just buy it.
Ready to install Newsbin? Go to Newsbin Installation Guide next.
Still have questions? Go read what others have to say: